The decision to undergo a tummy tuck represents a significant step toward restoring your body’s contour, but many patients discover that achieving truly transformative results requires more than just removing excess skin. For the 171,064 individuals who underwent abdominoplasty procedures in 2024, muscle repair emerged as a critical component of comprehensive abdominal restoration, particularly for those recovering from pregnancy or significant weight loss.
Modern tummy tuck procedures increasingly incorporate muscle repair techniques to address the underlying structural weaknesses that diet and exercise alone cannot correct. This comprehensive approach to body contouring has become especially relevant as the abdominoplasty market reaches $2.5 billion in 2025, driven by patients seeking both aesthetic improvement and functional core restoration.
At Kashaf Cosmetic Surgery, Dr. Kashaf Sherafgan specializes in combining advanced muscle repair techniques with traditional abdominoplasty to deliver results that go beyond surface-level improvements. Understanding how muscle repair enhances your tummy tuck outcome can help you make an informed decision about your body contouring journey.
Understanding Muscle Separation and Why Repair Matters
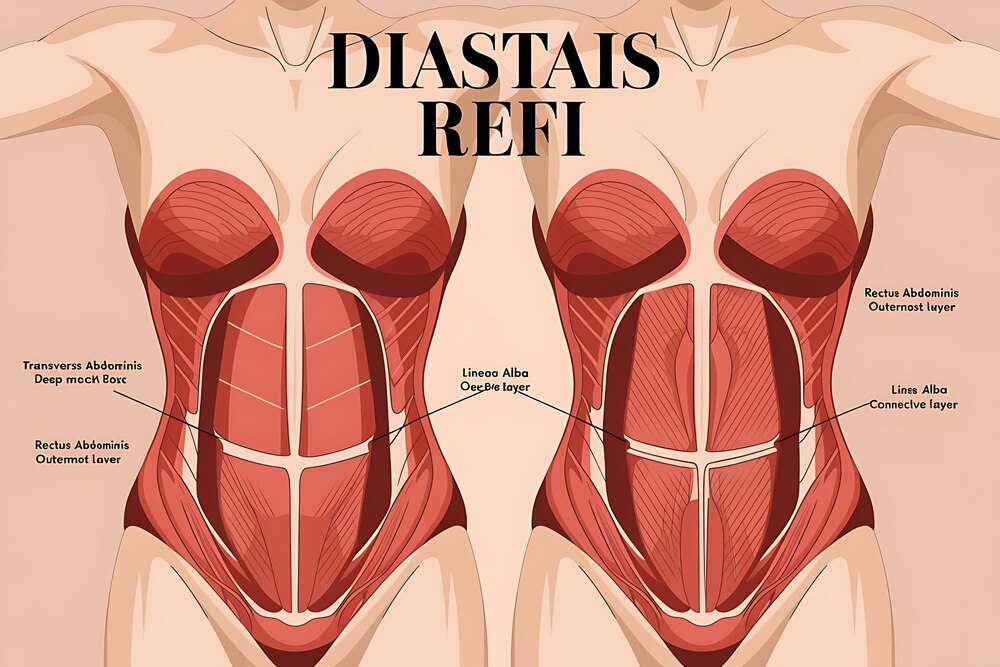
Abdominal muscle separation, medically known as diastasis recti, affects millions of adults and creates both aesthetic and functional challenges that extend far beyond appearance. The rectus abdominis muscles, which run vertically down your abdomen, can separate along the midline connective tissue called the linea alba, creating a gap that weakens your entire core structure.
This separation impacts more than just how your stomach looks. Patients with muscle separation often experience chronic back pain, poor posture, and difficulty with everyday activities like lifting or bending. The weakened abdominal wall can also contribute to digestive issues and pelvic floor dysfunction, making muscle repair during a tummy tuck both a cosmetic and functional necessity.
Research demonstrates that surgical muscle repair achieves an 85-90% long-term success rate for maintaining muscle integrity, offering patients lasting improvement in both core strength and abdominal appearance. This high success rate explains why muscle repair has become a standard component of comprehensive abdominoplasty procedures.
What Causes Abdominal Muscle Separation
Pregnancy remains the leading cause of diastasis recti, with the growing uterus stretching the abdominal muscles beyond their capacity to fully recover postpartum. Multiple pregnancies, carrying twins or triplets, and pregnancies later in life increase the likelihood and severity of muscle separation.
Significant weight fluctuations create similar stress on the abdominal wall. Rapid weight gain stretches the muscles and connective tissue, while subsequent weight loss leaves the muscles unable to return to their original position. Genetics also play a role, as some individuals naturally have weaker connective tissue that predisposes them to muscle separation.
Age-related changes in tissue elasticity and muscle tone contribute to progressive separation over time. Additionally, improper exercise techniques, particularly aggressive abdominal workouts without proper form, can worsen existing separation or create new muscle gaps.
Signs You Need Muscle Repair with Your Tummy Tuck
Physical symptoms often provide the clearest indication that muscle repair should accompany your tummy tuck procedure. A visible bulge or ridge running down the center of your abdomen when you sit up or strain indicates separated muscles. This bulge may become more pronounced after eating or at the end of the day.
Core weakness manifests in multiple ways beyond aesthetic concerns. Difficulty maintaining good posture, chronic lower back pain, and challenges with balance or stability during physical activities all suggest compromised abdominal muscles. Many patients report feeling like their internal organs lack proper support, creating a sensation of weakness or vulnerability in the midsection.
Aesthetic indicators include a protruding belly that persists despite weight loss or exercise, skin that appears loose or saggy even at a healthy weight, and an inability to achieve a flat stomach regardless of fitness level. These signs suggest that muscle repair surgery could significantly enhance your tummy tuck results.
The Muscle Repair Process During Abdominoplasty
Modern muscle repair during abdominoplasty involves sophisticated techniques that go beyond simple suturing. Surgeons now employ layered reinforcement methods that create lasting structural support while maintaining natural movement and flexibility. The process begins with careful assessment of the muscle separation extent and the surrounding fascia integrity.
During the procedure, your surgeon accesses the separated muscles through the standard tummy tuck incision, eliminating the need for additional cuts. The muscles are then brought together using permanent sutures in a technique that distributes tension evenly across the repair site, reducing the risk of future separation.
Advanced techniques now include fascia reinforcement, where the connective tissue surrounding the muscles receives additional support through specialized suturing patterns. This comprehensive approach addresses not just the muscle separation but also strengthens the entire abdominal wall structure.
Muscle Plication Technique Explained
Muscle plication represents the gold standard technique for repairing diastasis recti during abdominoplasty. The surgeon begins by identifying the edges of the separated rectus muscles, then uses permanent sutures to bring them back together along the midline. This process involves folding the stretched fascia over itself, creating a tighter, more supportive structure.
The suturing pattern typically follows a continuous technique from the bottom of the breastbone to the pubic area, ensuring uniform tension distribution. Multiple layers of sutures may be placed to provide additional strength and prevent future separation. The surgeon carefully adjusts the tension to create optimal contour while maintaining functional flexibility.
Some cases require additional lateral plication to address weakness in the oblique muscles or broader abdominal wall laxity. This comprehensive approach ensures that the entire core receives appropriate support and reinforcement.
Combined Procedures: Muscle Repair in Mommy Makeovers
The integration of muscle repair into mommy makeover procedures has become increasingly sophisticated in 2025, with surgeons coordinating multiple interventions to maximize results while minimizing recovery time. When combined with breast surgery and liposuction, muscle repair requires careful surgical planning to ensure optimal healing and aesthetic outcomes.
Timing and sequencing prove critical when incorporating muscle repair into comprehensive body contouring. Surgeons typically perform the muscle repair early in the procedure when tissues are fresh and responsive, followed by skin removal and contouring. This approach allows for precise adjustment of skin tension based on the newly tightened muscle structure.
Recovery coordination becomes essential when multiple procedures are performed simultaneously. The muscle repair component often dictates activity restrictions and recovery timeline, requiring patients to plan for the extended healing period necessary for proper muscle integration.
Post-Weight Loss Muscle Repair: The GLP-1 Connection
The surge in GLP-1 medication use has created a new category of muscle repair candidates. According to recent data from the American Society of Plastic Surgeons, 20% of patients prescribed GLP-1 medications have already undergone plastic surgery, with 39% actively considering procedures to address the physical changes from rapid weight loss.
Rapid weight loss from medications like Ozempic and Wegovy creates unique tissue changes that affect muscle repair requirements. The accelerated fat loss often leaves muscles stretched and weakened, unable to contract effectively even after achieving goal weight. This creates a distinct surgical challenge requiring specialized techniques to restore both form and function.
Dr. Kashaf Sherafgan at Kashaf Cosmetic Surgery has developed specific protocols for addressing the muscle laxity common in post-GLP-1 patients, recognizing that traditional repair techniques may need modification to accommodate the altered tissue characteristics these medications create.
Why Ozempic and Semaglutide Patients Need Specialized Muscle Repair
GLP-1 medications induce rapid weight loss that outpaces the body’s natural ability to adapt, leaving muscles and connective tissues unable to contract to their new dimensions. The medications’ effect on muscle mass preservation varies among patients, with some experiencing significant muscle loss alongside fat reduction, creating additional weakness requiring surgical correction.
The skin and fascia changes associated with medication-induced weight loss differ from traditional weight loss patterns. Patients often present with more uniform tissue laxity rather than localized problem areas, necessitating comprehensive muscle wall reconstruction rather than targeted repair.
Additionally, the metabolic changes induced by GLP-1 medications can affect healing and tissue recovery, requiring surgeons to adjust their surgical techniques and post-operative protocols. Understanding these unique factors ensures optimal outcomes for this growing patient population.
Timing Your Muscle Repair After Weight Loss
Weight stability represents the primary factor in determining optimal timing for muscle repair surgery. Surgeons typically recommend maintaining your goal weight for at least three to six months before proceeding with surgery. This stabilization period allows tissues to settle and ensures that surgical results will be long-lasting.
Nutritional optimization becomes crucial during this waiting period. Post-weight loss patients often require supplementation to support proper healing, particularly protein intake to maintain muscle mass and vitamins to support tissue repair. Working with a nutritionist familiar with post-bariatric or GLP-1 patient needs can significantly improve surgical outcomes.
The psychological readiness for surgery also factors into timing decisions. Patients should feel comfortable with their new body weight and have realistic expectations about what muscle repair can achieve. This mental preparation contributes to satisfaction with results and compliance with post-operative care requirements.
Recovery Timeline and Expected Results
Recovery from muscle repair tummy tuck follows a predictable trajectory, though individual healing rates vary based on factors including age, overall health, and the extent of repair required. The initial two to four weeks represent the critical healing phase when the repaired muscles begin integrating with surrounding tissues.
Most patients experience peak discomfort during the first week, particularly when moving from lying to sitting positions. This discomfort stems from the tightened muscles adjusting to their new position and the body adapting to improved core support. Pain management protocols have advanced significantly, with many surgeons now employing long-acting local anesthetics and muscle relaxants to enhance comfort.
Return to normal activities occurs gradually, with most patients resuming light daily activities within two weeks and returning to work within three to four weeks for non-physical jobs. Complete healing and final results typically become apparent at the six-month mark, when swelling fully resolves and tissues settle into their new configuration.
First Month: Critical Healing Phase
Week one focuses on rest and initial healing, with patients maintaining a slightly bent posture to minimize tension on the repair site. Compression garments provide essential support during this phase, helping to reduce swelling and support the newly tightened muscles. Walking short distances several times daily promotes circulation and prevents complications.
During week two, patients typically experience decreased discomfort and increased mobility. The drainage tubes, if placed, are usually removed, and patients can begin showering normally. Light stretching exercises may be introduced under medical supervision to prevent stiffness while protecting the repair.
Weeks three and four mark the transition to increased activity. Patients can usually stand fully upright and resume most non-strenuous daily activities. Driving becomes possible once patients can react quickly without discomfort. However, lifting restrictions remain in place to protect the healing muscle repair.
Long-Term Success Rates and Muscle Integrity
Clinical data demonstrates impressive long-term success rates for muscle repair during tummy tuck procedures, with 85-90% of patients maintaining excellent muscle integrity five years post-surgery. These statistics reflect both the durability of modern repair techniques and the importance of proper patient selection and preparation.
Factors affecting long-term success include adherence to post-operative restrictions, maintenance of stable body weight, and avoidance of subsequent pregnancies. Patients who follow their surgeon’s guidelines and maintain a healthy lifestyle typically enjoy permanent improvement in both muscle function and aesthetic appearance.
Regular follow-up assessments help identify any concerns early, though revision rates remain low. Most patients report sustained improvement in core strength, posture, and overall quality of life, validating the functional benefits of muscle repair beyond cosmetic enhancement.
Cost Considerations and Market Trends for 2025
The global abdominoplasty market valued at $2.5 billion in 2025 reflects growing demand for comprehensive body contouring procedures. Muscle repair adds complexity and operative time to standard tummy tuck procedures, influencing overall costs and requiring careful financial planning.
Regional variations in pricing reflect differences in surgeon expertise, facility costs, and market demand. Metropolitan areas with high concentrations of board-certified plastic surgeons often command premium prices, though they may also offer more advanced techniques and technology. Understanding these market dynamics helps patients budget appropriately for their procedure.
Financing options have expanded to meet growing demand, with many practices offering payment plans and working with medical financing companies. These arrangements make muscle repair tummy tucks accessible to a broader range of patients seeking comprehensive abdominal restoration.
Muscle Repair Impact on Total Procedure Cost
Adding muscle repair to a standard tummy tuck typically increases surgical time by 30 to 60 minutes, depending on the extent of separation and repair technique employed. This additional time translates to increased operating room fees, anesthesia costs, and surgeon fees, generally adding 15-25% to the base procedure cost.
The complexity of muscle repair also influences post-operative care requirements. Patients may require additional follow-up appointments, specialized compression garments, and extended pain management protocols. These factors should be considered when budgeting for the complete treatment process.
Despite higher upfront costs, muscle repair often proves cost-effective long-term by addressing functional issues that might otherwise require separate treatment. The combined aesthetic and functional improvements justify the investment for most patients seeking comprehensive abdominal restoration.
Insurance Coverage for Functional Muscle Repair
Insurance coverage for muscle repair remains limited but possible when medical necessity can be documented. Severe diastasis recti causing functional impairment, chronic pain, or herniation may qualify for partial coverage under certain insurance plans. Documentation requirements typically include physical therapy records, imaging studies, and detailed symptom documentation.
The key to potential coverage lies in establishing the functional rather than cosmetic nature of the repair. Working with a surgeon experienced in insurance documentation can improve the likelihood of approval. Some patients successfully obtain coverage for the muscle repair portion while self-paying for the cosmetic components of their procedure.
Even when insurance denies coverage, having comprehensive documentation can support tax deductions for medical expenses or flexible spending account reimbursement. Patients should consult with their insurance providers and tax advisors to understand available options.
Choosing the Right Surgeon for Muscle Repair Tummy Tuck
Selecting a surgeon with specific expertise in muscle repair techniques significantly impacts your surgical outcome. Board certification in plastic surgery provides the foundation, but additional training in advanced abdominoplasty techniques and experience with complex reconstructions indicate superior qualifications.
During consultations, inquire about the surgeon’s specific approach to muscle repair, including their preferred techniques and how they customize treatment based on individual anatomy. Request before and after photos specifically showing muscle repair results, not just standard tummy tuck outcomes. Understanding their revision rate and how they handle complications provides insight into their expertise level.
At Kashaf Cosmetic Surgery, Dr. Kashaf Sherafgan combines extensive training in advanced muscle repair techniques with a personalized approach to each patient’s unique needs. The practice’s commitment to comprehensive evaluation and customized treatment planning ensures optimal outcomes for patients seeking muscle repair with their tummy tuck procedure.
Conclusion: Making Your Muscle Repair Decision
The integration of muscle repair into your tummy tuck procedure represents an investment in both form and function, addressing the underlying structural issues that contribute to abdominal weakness and aesthetic concerns. With success rates approaching 90% for long-term muscle integrity, this comprehensive approach offers lasting solutions for patients affected by pregnancy, weight loss, or age-related changes.
As you consider your options for abdominal restoration in 2025, remember that muscle repair extends beyond cosmetic improvement to enhance core strength, improve posture, and potentially alleviate chronic pain. The decision to include muscle repair should be based on a thorough evaluation of your individual anatomy, functional concerns, and aesthetic goals. If you’re ready to explore how muscle repair can enhance your tummy tuck results, contact Kashaf Cosmetic Surgery to schedule a consultation with Dr. Kashaf Sherafgan and discover the transformative potential of comprehensive abdominal restoration.